What is Passivhaus?

The term Passive House (Passivhaus in German) stands for standard of house building. Passivhaus standard means using energy efficiency in the building which results in reducing its energy use. Passivhaus building is ultra-low energy building that requires small amount of energy for space heating or cooling. Passivhaus can be applied to new buildings, but it can be also used for refurbishing old ones.
The Passivhaus standard for central Europe requires that the building fulfills following requirements:
1. building must be designed to have an annual heating demand as calculated with the Passivhaus Planning Package of not more than 15 kWh/m² per year in heating and 15 kWh/m² per year cooling energy OR to be designed with a peak heat load of 10W/m²,
2. total primary energy (source energy for electricity etc.) consumption (primary energy for heating, hot water and electricity) must not be more than 120 kWh/m² per year,
3. the building must not leak more air than 0.6 times the house volume per hour (n50 ≤ 0.6 / hour) at 50 Pa (N/m²) as tested by a blower door.
The Passivhaus standard for central Europe requires that the building fulfills following requirements:
1. building must be designed to have an annual heating demand as calculated with the Passivhaus Planning Package of not more than 15 kWh/m² per year in heating and 15 kWh/m² per year cooling energy OR to be designed with a peak heat load of 10W/m²,
2. total primary energy (source energy for electricity etc.) consumption (primary energy for heating, hot water and electricity) must not be more than 120 kWh/m² per year,
3. the building must not leak more air than 0.6 times the house volume per hour (n50 ≤ 0.6 / hour) at 50 Pa (N/m²) as tested by a blower door.
Project Passivhaus in Serbia

Project included building suburban estate, made of several dozen same type houses. Each house was built to fulfill Passivhaus standard in each of those 3 energy spending points. Each house has two floors, 3 bedrooms, 2 bathrooms, living and dining area and a kitchen. Houses were built to form a cascade, so every family can have it's own privacy. Roof has grass planted, as an extensive green roof type, so it can keep cool upper floor of the building and, also, to reduce energy losses trough ceiling. Every roof has solar panels for hot domestic water. Houses can be equipped, additionally, with PV panels and electric energy can be sold to local utility. South side of each house has construction that throws shadows on windows and doors during summer, so house doesn't overheat. During winter, sun is lower on horizon, so sunlight can enter the house and it is used for passive heating.
House project was done by Natasa Pavic, Master in Architecture.
House project was done by Natasa Pavic, Master in Architecture.
Investment analisys
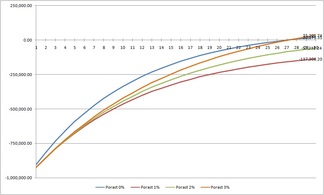
Investment analysis
Investment analysis was made by comparing two houses. One was made traditionally masonry and the other by Passivhaus standard, was made like a prefabricated mounted house using large panel system. Starting point of analysis was the difference in house pricing, as shown on graph. There are 4 lines on the graph - each one represents different electricity price increase rate - 0, 1, 2 and 3 % annually. Graph shows that investment can not return because of 3 reasons:
- electricity price in Serbia is low and Passivhaus standard requires expensive technology and building,
- inflation rate in Serbia is about 10% annually,
- there are no subsidizing measures by government.
- electricity price in Serbia is low and Passivhaus standard requires expensive technology and building,
- inflation rate in Serbia is about 10% annually,
- there are no subsidizing measures by government.



